September equinox 2024
When is the September equinox 2024?
The September equinox 2024 is on Sunday, September 22, 2024 (in 149 days). Calendar for 2024
Please note: The dates given on this page are based on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which for practical purposes is equivalent to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). While the September equinox occurs at the same moment in time all over the world, the date and local time differ from location to location depending on a location's time zone. For more details see the explanations below.
Sponsored links
What is the September equinox?
 The September equinox marks the beginning of autumn in the Northern Hemisphere
The September equinox marks the beginning of autumn in the Northern HemisphereThe September equinox usually occurs every year between September 21 and 24. The dates given on this page are based on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which for practical purposes is equivalent to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT - the time zone of the United Kingdom). While the September equinox occurs at the same moment in time all over the world, the date and local time differ from place to place depending on the year and a location's time zone. For locations that are ahead of UTC (further east) it may fall on the day after, and for locations that are behind UTC (further west) it may fall on the day before. To find out the exact date and time of the September equinox 2024 in your area use this seasons calculator.
The September equinox is one of four days with solar events (two equinoxes and two solstices) throughout the year that mark the beginning of a new season. The other days are the March equinox, the June solstice and the December solstice.
The word "equinox" is derived from Latin and means "equal night". On the day of an equinox, day and night are of approximately equal length all over the world, as the Earth's rotational axis is neither tilted away from nor towards the Sun. At all other times the length of day and night will be different.
The exact moment of the September equinox through the centuries
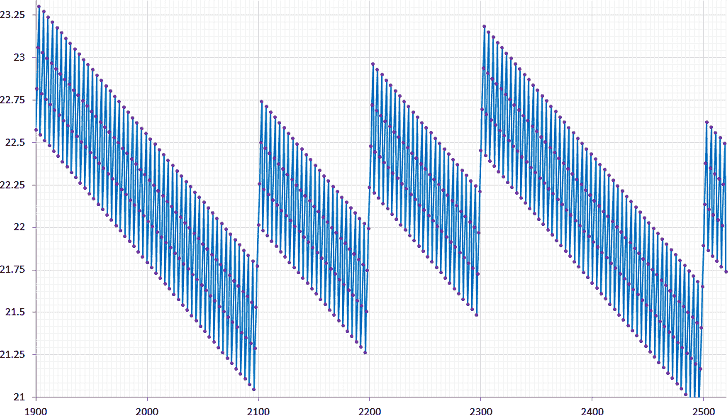
Graph demonstrating the movement (caused by leap shifting) of the exact moment of the September equinox between 1900 and 2520. X axis (bottom, horizontal): Calendar years, Y axis (left, vertical): day in September (21 to 23).
In a non-leap year, the moment of the September equinox is about 5 hours 49 minutes after that moment in the previous year (in UTC), and in a leap year it is about 18 hours 11 minutes before that moment in the previous year, as can be seen in this graph. In this way the time of the September equinox constantly shifts back and forth so it always stays between September 21 and 24. This four year cycle is clearly visible in the graph.
To adjust for the gradual movement backwards on the calendar (as visible for the period 1900 to 2099), in years divisible by 100 (1900, 2100, 2200, 2300 and 2500 on the graph), which should be leap years as they are divisible by 4, the leap day is omitted (except when they are divisible by 400, eg. 2000 and 2400) and the moment of the September equinox moves forward in time compared to the same moment in the year before.
Further reading:
- September equinox on Wikipedia
- Equinoxes in general on Wikipedia
Overview: seasons, equinoxes and solstices
Dates shown apply to the Northern Hemisphere and are based on UTC (GMT)| Season | Start | End |
| Spring | Spring equinox (vernal equinox, March equinox) March 19 to 21 |
Summer solstice (June solstice) June 20 to 22 |
| Summer | Summer solstice (June solstice) June 20 to 22 |
Autumn equinox (Fall equinox, September equinox) September 21 to 24 |
| Autumn (Fall) |
Autumn equinox (Fall equinox, September equinox) September 21 to 24 |
Winter solstice (December solstice) December 20 to 23 |
| Winter | Winter solstice (December solstice) December 20 to 23 |
Spring equinox (vernal equinox, March equinox) March 19 to 21 |
When is the September equinox 2025?
The September equinox 2025 is on Monday, September 22, 2025 (in 514 days). Calendar for 2025
Dates for the September equinox in other years
The next occurrence of the September equinox is marked in red.| When is ...? | Date | Day of the week | Days away |
| September equinox 2019 | September 23, 2019 | Monday | 1677 days ago |
| September equinox 2020 | September 22, 2020 | Tuesday | 1312 days ago |
| September equinox 2021 | September 22, 2021 | Wednesday | 947 days ago |
| September equinox 2022 | September 23, 2022 | Friday | 581 days ago |
| September equinox 2023 | September 23, 2023 | Saturday | 216 days ago |
| September equinox 2024 | September 22, 2024 | Sunday | in 149 days |
| September equinox 2025 | September 22, 2025 | Monday | in 514 days |
| September equinox 2026 | September 23, 2026 | Wednesday | in 880 days |
| September equinox 2027 | September 23, 2027 | Thursday | in 1245 days |
| September equinox 2028 | September 22, 2028 | Friday | in 1610 days |
| September equinox 2029 | September 22, 2029 | Saturday | in 1975 days |
Data provided 'as is' without warranty |
|||
Dates of the September equinox 2024 and surrounding years as downloadable image file
Printable 2024 Calendars for Word, Excel and PDF
Free printable 2024 calendar templates
A selection of downloadable, printable calendar templates for 2024 with US federal holidays, suitable for a variety of applications. Available for Word, Excel and PDF.Word |
Excel |
Dates of other holidays, events and celebrations
Calendar templates
Home · Sitemap / archive
Yearly calendars
Quarterly calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Monthly calendars
Mar · Apr · May · Jun · Jul Weekly calendars
Daily calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Hourly calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Split year calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
School calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
Academic calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
Fiscal calendars 2024
PDF · Word · Excel
2 year calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
3 year calendars 24-26
PDF · Word · Excel
Photo calendars 2024
PDF · Word · Excel
Birthday calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Blank calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Perpetual calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Yearly calendars
| PDF: | 2024 · 2025 / 2026 |
| Word: | 2024 · 2025 / 2026 |
| Excel: | 2024 · 2025 / 2026 |
PDF · Word · Excel
Monthly calendars
Mar · Apr · May · Jun · Jul Weekly calendars
| PDF: | 2024 · 2025 / 2023 |
| Word: | 2024 · 2025 / 2023 |
| Excel: | 2024 · 2025 / 2023 |
PDF · Word · Excel
Hourly calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Split year calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
School calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
Academic calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
Fiscal calendars 2024
PDF · Word · Excel
2 year calendars 24/25
PDF · Word · Excel
3 year calendars 24-26
PDF · Word · Excel
Photo calendars 2024
PDF · Word · Excel
Birthday calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Blank calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Perpetual calendars
PDF · Word · Excel
Online Calendars
More...